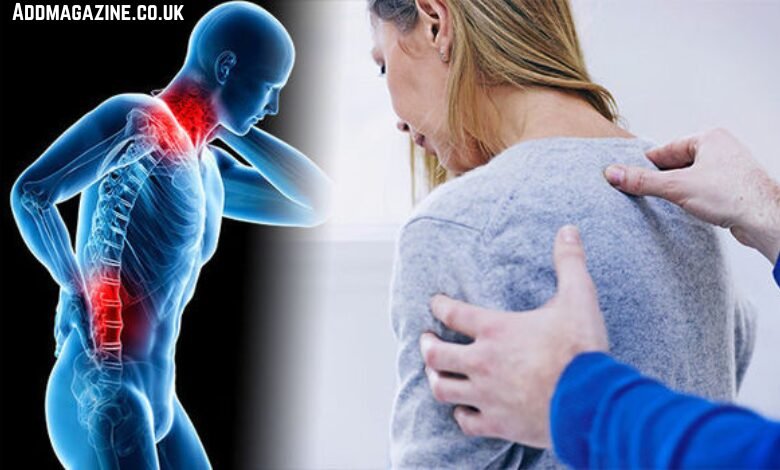
Inomyalgia is a complex condition that involves widespread muscle pain, stiffness, and a lack of energy, affecting individuals physically and mentally. Though not a widely recognized term in medical science, the symptoms of Inomyalgia are very real and can severely impact a person’s daily life. This article aims to provide an in-depth look at the potential causes, common symptoms, and possible management strategies for those dealing with this muscle-related condition.
What is Inomyalgia?
Inomyalgia appears to be a term describing a muscle-related condition that involves widespread pain, stiffness, and a general lack of energy. While this term is not universally recognized in medical literature, it can be understood as a syndrome that affects the muscles and may share similarities with well-known conditions like fibromyalgia.
Unlike fibromyalgia, which can be triggered by a variety of factors, Inomyalgia seems to have its unique set of symptoms, progression patterns, and potential causes.
People suffering from Inomyalgia report persistent pain in different areas of the body, as well as accompanying symptoms like morning stiffness, fatigue, and brain fog. The chronic nature of the pain can also lead to emotional symptoms, such as anxiety or stress, which can further contribute to the cycle of discomfort.
Understanding Inomyalgia: A Definition
Inomyalgia can be defined as a syndrome characterized by chronic muscle pain and discomfort that persists over time. The pain can be widespread or localized, affecting different muscle groups in the body. It is often associated with symptoms such as fatigue, stiffness, and sleep disturbances. While it shares some similarities with conditions like fibromyalgia, Inomyalgia appears to have its unique triggers, progression patterns, and associated symptoms.
Unlike conditions that might primarily target joints or organs, Inomyalgia centers around the muscles. For many individuals, the condition becomes a burden not only on their physical health but also on their mental and emotional well-being.
What Are the Causes of Inomyalgia?
Understanding the root causes of Inomyalgia is essential in managing the condition. Several factors may contribute to the development of Inomyalgia. These causes often overlap and work together to exacerbate the condition.
1. Genetic Predisposition
In some cases, family history plays a key role in whether an individual develops Inomyalgia. A genetic predisposition to muscle-related pain syndromes increases the likelihood of developing chronic pain conditions like Inomyalgia. If there is a family history of fibromyalgia or similar disorders, the risk of developing Inomyalgia may be higher.
2. Stress and Emotional Pressure
Chronic stress can have significant effects on the body, particularly on muscle relaxation. Stress often causes the muscles to stay in a state of constant tension, leading to muscle strain and pain. Additionally, emotional stress can disrupt energy balance, making the body more susceptible to conditions like Inomyalgia.
3. Poor Posture
Long periods of sitting or standing with improper posture can put additional strain on muscles, leading to chronic muscle tension and pain. In individuals with Inomyalgia, poor posture may exacerbate these symptoms, making it difficult to find comfort.
4. Nutritional Deficiencies
A lack of essential vitamins and minerals, such as vitamin D, vitamin B12, and magnesium, can impair muscle function and lead to persistent pain. These nutrients are crucial for muscle relaxation and repair. Without adequate amounts, muscle regeneration may be hindered, leading to discomfort and fatigue.
5. Sleep Disorders
Sleep plays a critical role in the body’s ability to repair muscle tissue. Insufficient sleep prevents the body from healing, contributing to chronic muscle pain. Sleep disturbances are common in individuals with Inomyalgia, leading to further exhaustion and aggravation of symptoms.
6. Hormonal Imbalance
Fluctuations in hormones, especially cortisol and serotonin, can influence muscle function. High cortisol levels caused by stress can lead to muscle tension and pain. On the other hand, low serotonin levels may worsen the sensitivity to pain, making the discomfort more difficult to manage.
What Are the Symptoms of Inomyalgia?
The symptoms of Inomyalgia can vary from person to person, but there are some key signs that are commonly reported. These symptoms can have a significant impact on daily life, and it is essential to be aware of them to seek proper treatment.
1. Persistent Muscle Pain
The primary symptom of Inomyalgia is widespread muscle pain that may affect different parts of the body. The pain can be either localized in specific areas or more generalized, covering large regions of the body. The discomfort can range from mild to severe and is typically chronic, lasting for extended periods.
2. Morning Stiffness
Many individuals with Inomyalgia experience morning stiffness, which makes it difficult to start the day. This stiffness can make simple tasks, such as getting out of bed or getting dressed, feel incredibly challenging. It often improves with movement but can return after long periods of rest.
3. Fatigue
Fatigue is one of the hallmark symptoms of Inomyalgia. Chronic exhaustion that doesn’t improve with rest is common. This constant fatigue can disrupt daily routines and significantly lower overall efficiency. The body’s inability to fully rest and recover due to muscle pain can lead to an ongoing sense of tiredness.
4. Brain Fog
Another common symptom associated with Inomyalgia is brain fog—a cognitive condition characterized by trouble concentrating, memory issues, and a general feeling of mental cloudiness. This can make it hard to focus on tasks or retain information, leading to frustration and difficulty managing day-to-day responsibilities.
5. Sensitivity to Temperature Changes
People with Inomyalgia often report being sensitive to cold or sudden temperature changes. For some, cold weather can trigger more severe muscle pain and discomfort. The body’s inability to regulate temperature effectively can add another layer of distress for individuals dealing with this condition.
6. Sleep Disturbances
The pain and discomfort from Inomyalgia can lead to significant sleep disturbances. Insufficient sleep prevents the muscles from recovering and makes the body more susceptible to fatigue. This creates a vicious cycle where poor sleep contributes to increased pain, which in turn makes it harder to rest.
Managing Inomyalgia: Treatment and Lifestyle Adjustments
Although there is no cure for Inomyalgia, there are several ways to manage the symptoms and improve quality of life. Treatment often focuses on reducing pain, improving sleep, and managing stress.
1. Stress Management Techniques
Since stress can worsen Inomyalgia, practicing stress reduction techniques such as meditation, deep breathing exercises, and mindfulness can help ease muscle tension and improve overall well-being.
2. Posture Correction
Improving posture through ergonomic adjustments and regular stretching exercises can help reduce strain on the muscles. It’s important to be mindful of posture throughout the day, especially for those who sit for extended periods.
3. Nutrition and Supplements
Ensuring adequate intake of vitamins and minerals, particularly magnesium, vitamin D, and B12, can help manage muscle pain. A diet rich in anti-inflammatory foods can also reduce overall discomfort.
4. Exercise and Physical Therapy
Low-impact exercises, such as swimming or walking, can help strengthen muscles and alleviate pain. In some cases, physical therapy may be recommended to target specific areas of tension and improve flexibility.
5. Sleep Improvement
Improving sleep hygiene is crucial for managing Inomyalgia. Ensuring a comfortable sleep environment and establishing a regular sleep schedule can help reduce fatigue and improve muscle regeneration.
6. Medications
In some cases, medications such as pain relievers, muscle relaxants, or anti-inflammatory drugs may be prescribed to help manage pain. It’s important to seek advice from a healthcare provider before beginning any new medication.
Conclusion
Inomyalgia is a challenging condition that affects both the muscles and the mind. Its exact causes are multifactorial, and its symptoms can vary from person to person. However, by understanding the causes and symptoms, and by implementing effective treatment strategies, individuals can manage their condition and improve their quality of life. If you suspect you are suffering from Inomyalgia, seeking medical advice and addressing lifestyle factors such as posture, stress, nutrition, and sleep are key steps toward managing the condition effectively.