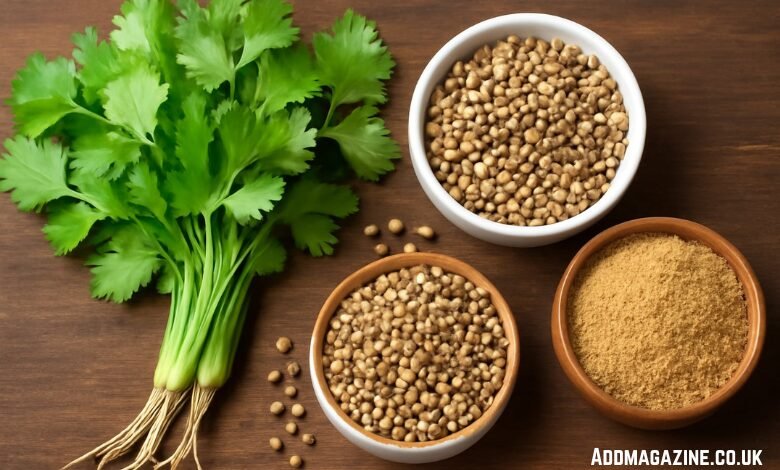
Koriandri, also known as coriander, is a herb with rich culinary and medicinal significance. The name “koriandri” is commonly used in South Asian and Middle Eastern cultures, but the plant is known by many different names in various parts of the world. It’s not only valued for its fresh, aromatic leaves (called cilantro in some places) but also for its seeds, which are widely used as a spice. Let’s delve deeper into the origins, historical significance, and global names of koriandri.
1. What is Koriandri?
Koriandri (Coriandrum sativum) is a one-year herb belonging to the Apiaceae family, known for its aromatic leaves and seeds. It is native to regions spanning from Southern Europe to North Africa and southwestern Asia. Both the leaves and seeds of the plant are utilized in cooking, making it a versatile herb. While the fresh leaves are commonly used in salads, garnishes, or as a seasoning, the seeds are dried and ground to be used as a spice. The plant’s distinct aroma has made it a staple in many cuisines around the world, especially in South Asian, Middle Eastern, and Latin American cooking.
The plant is known for its unique combination of citrus and earthy flavors, with a slightly spicy and pungent kick that adds a depth of flavor to various dishes. Beyond its culinary use, koriandri has also been employed for medicinal purposes for centuries. Its purported health benefits include aiding digestion, reducing inflammation, and even helping with anxiety and insomnia.
2. Origins and History of Koriandri
Koriandri has a long history that dates back thousands of years. The earliest known use of coriander dates back to around 5,000 BC, where it was cultivated in ancient Egypt. Archaeological evidence suggests that coriander was used both as a culinary herb and as a medicinal plant. It was even found in the tomb of Tutankhamun, illustrating its significance in ancient Egyptian culture.
From Egypt, koriandri spread throughout the Mediterranean and into Europe and Asia. Ancient Greek and Roman civilizations used it extensively for both flavoring food and for its purported health benefits. The name “coriander” itself is derived from the Greek word koriannon, which is thought to come from the word koris, meaning “bedbug.” This is due to the plant’s strong smell, which was likened to the odor of a bug. Interestingly, the term “coriander” is used primarily to refer to the seeds of the plant, whereas the leaves are known as cilantro in many parts of the world.
3. The Name “Koriandri” and Its Global Usage
The name “koriandri” is used predominantly in South Asian countries like India, Pakistan, and Bangladesh. It’s a commonly used term in these regions due to the herb’s widespread cultivation and use in traditional cuisines. In these cultures, koriandri is indispensable in both savory and sweet dishes, and is often a key ingredient in spice mixes, curries, and chutneys.
The name “koriandri” itself is rooted in several different languages. For instance, in Hindi and Urdu, it is referred to as koriandri. In other languages spoken in the region, such as Punjabi and Gujarati, it is also called hara dhaniya (referring to the fresh leaves) or simply dhania.
In Western countries, the term “coriander” is used predominantly for the seeds, while “cilantro” refers to the fresh leaves. The word “cilantro” comes from the Spanish language, which is influenced by the plant’s introduction to the Americas during European colonization. Over time, the name “cilantro” became widely used in Latin American countries and parts of the United States.
In the Middle East, coriander has various names depending on the region. In Arabic, it’s called kuzbara. And in Persian, it is referred to as gashniz or kinwa, and in Turkish, it is known as kimyon. These names reflect the plant’s extensive cultivation and use across these regions.
4. The Linguistic and Cultural Significance of Koriandri
The widespread use of koriandri in different cultures highlights its importance as both a culinary and medicinal herb. Its use in ancient civilizations, especially in the Mediterranean, shows how integral the herb was to early food cultures. Today, it remains a fundamental part of cuisine in many parts of the world.
In India and Pakistan, koriandri is deeply embedded in the daily culinary practices. It’s a common ingredient in curries, pickles, dals (lentil stews), and vegetable dishes. The herb is also used in Indian street foods like chaat, where the fresh leaves are mixed with tamarind, yogurt, and spices for a flavorful snack.
Similarly, in Middle Eastern cooking, koriandri plays a prominent role. It is used in various traditional dishes like tabbouleh, falafel, and hummus. The ground seeds are also used in spice blends such as garam masala and baharat, which add warmth and depth to the cuisine.
5. Where Koriandri is Grown
Koriandri is a herb that thrives in temperate climates and can be found growing in a variety of regions worldwide. Its native habitat spans across parts of Europe, the Mediterranean, and Asia, but it is now widely cultivated in many other countries due to its global popularity.
In India, Pakistan, and Bangladesh, koriandri is commonly grown in household gardens, as well as larger agricultural fields. In fact, India is one of the largest producers of coriander in the world. Similarly, countries like China, Turkey, Morocco, and Egypt also cultivate coriander, often for both domestic use and export.
In the United States, cilantro is grown primarily in California, where the climate is ideal for its growth. Mexico is another major producer of coriander, especially for the fresh leaves, which are a key component of Mexican cuisine.
6. Varieties of Koriandri
Koriandri is a versatile herb with different varieties and uses, depending on the part of the plant. The fresh leaves, commonly known as cilantro, have a much milder and fresher flavor compared to the seeds, which are more pungent and citrusy. The seeds, when dried and ground, have a warm, spicy flavor with a hint of citrus. They are commonly used in spice mixes, soups, stews, and curries.
In addition to its leaves and seeds, the root of the coriander plant is used in some culinary traditions, especially in Thai and Southeast Asian cuisines. The roots have a more earthy and intense flavor and are often used to make pastes or in marinades.
7. The Health Benefits of Koriandri
Beyond its culinary value, koriandri has long been used in traditional medicine for its various health benefits. It is believed to have antibacterial and antifungal properties, which make it useful in treating digestive issues, such as indigestion, bloating, and flatulence.
Studies have shown that koriandri has antioxidant properties, which help to neutralize free radicals in the body. Additionally, koriandri is often recommended as a natural remedy for anxiety and insomnia due to its calming effects.
Some studies suggest that koriandri may also have benefits for lowering blood sugar levels, making it an important herb for people with diabetes or those at risk of developing it. It is also considered a good source of dietary fiber, vitamins A, C, and K, and essential minerals like potassium and iron.
8. Uses of Koriandri (Coriander)
Koriandri, or coriander, is an incredibly versatile herb, and its uses go far beyond just being a garnish. From culinary delights to medicinal applications, koriandri plays an essential role in various cultures worldwide. Here’s a deeper dive into how koriandri is used and why it’s so widely appreciated.
Culinary Uses
Fresh Leaves (Cilantro):
The fresh leaves of koriandri, often referred to as cilantro in many countries, are commonly used in a wide array of cuisines, particularly in South Asian, Latin American, and Middle Eastern dishes. In India, Pakistan, and Bangladesh, cilantro is a staple, used in curries, soups, and chutneys. The leaves are also used to garnish dishes such as biryanis, dals (lentil stews), and kebabs, adding a refreshing flavor that balances spicier elements in the dish.
In Mexican cuisine, cilantro is an essential component of salsas, guacamole, tacos, and other traditional foods. The bright, citrusy flavor of cilantro complements the rich and hearty textures of these dishes.
Dried Seeds (Coriander Seeds):
The dried seeds of koriandri are a crucial component of many spice blends, such as garam masala, baharat, and curry powder. When ground, coriander seeds provide a mild, earthy, and slightly citrusy flavor. This makes them ideal for adding depth to stews, curries, marinades, and roasted meats.
Roots of Coriander:
In Thai and other Southeast Asian cuisines, coriander roots are valued for their strong, aromatic flavor. They are often pounded into a paste along with garlic and other spices to form the base for many dishes such as curries and soups.
Essential Oils:
Coriander essential oil, extracted from the seeds and sometimes from the leaves, is used in aromatherapy. The oil is believed to have antiseptic, anti-inflammatory, and relaxing properties. It’s often used in skin-care products, adding fragrance and offering soothing benefits.
Medicinal Uses
In traditional medicine, koriandri has been used for centuries to address a variety of health concerns. While not a substitute for professional medical treatment, coriander has several beneficial properties:
Digestive Aid:
Koriandri is known for its ability to stimulate digestion and ease stomach discomfort. The herb can help alleviate issues like indigestion, bloating, and flatulence. It contains compounds that promote the secretion of digestive enzymes, making it effective for improving overall digestion.
Anti-inflammatory Properties:
Both the fresh leaves and dried seeds of coriander have anti-inflammatory effects. These properties can be particularly useful in treating conditions like arthritis, where inflammation is a major cause of pain and discomfort.
Detoxification:
Coriander is often used as a detoxifying agent in traditional medicine. The herb is believed to help cleanse the body by promoting the removal of heavy metals, such as mercury, through urine. This is why it’s often included in cleansing diets.
Blood Sugar Regulation:
Some studies suggest that koriandri may help regulate blood sugar levels, making it beneficial for individuals with diabetes. The seeds have been shown to possess insulin-like properties, helping to lower blood sugar and improve overall glucose metabolism.
Antioxidant Benefits:
Coriander is rich in antioxidants like flavonoids, which protect the body from oxidative stress caused by free radicals. These antioxidants help prevent cell damage and may reduce the risk of chronic diseases, including cancer.
9. Nutritional Profile of Koriandri
Coriander is not only delicious but also packed with nutrients that contribute to overall health. The herb is a rich source of vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants that provide a wide range of benefits.
Vitamins and Minerals:
Coriander leaves are a good source of Vitamin K, which is important for bone health and blood clotting. They also contain significant amounts of Vitamin C, a powerful antioxidant that supports the immune system, and Vitamin A, which promotes healthy vision.
The seeds are an excellent source of dietary fiber, which aids in digestion and helps maintain a healthy gut. They also contain essential minerals such as calcium, potassium, magnesium, and iron. These minerals are vital for maintaining healthy bodily functions, including heart health, muscle function, and oxygen transport in the blood.
Essential Oils:
The essential oils found in coriander, including linalool and geraniol, have antibacterial and anti-inflammatory properties. These oils can help soothe the body and mind, providing stress-relief benefits when used in aromatherapy.
10. Advantages of Koriandri
There are several reasons why koriandri is a preferred herb in both the culinary world and traditional medicine. Its multiple health benefits and versatile usage make it a valuable addition to any kitchen or wellness routine.
1. Rich in Nutrients
Coriander provides essential nutrients that support various bodily functions. Its high content of vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants helps strengthen the immune system, improve skin health, and enhance bone strength. It is also a good source of dietary fiber, which contributes to digestive health.
2. Supports Digestive Health
As mentioned earlier, koriandri is well-known for its digestive benefits. It can help reduce bloating, gas, and discomfort after meals. Its mild antispasmodic properties relax the muscles in the stomach and intestines, making it easier to digest food and absorb nutrients.
3. Anti-inflammatory and Antioxidant Properties
The anti-inflammatory properties of koriandri can help alleviate pain and swelling in conditions like arthritis. Additionally, its antioxidant-rich profile helps prevent cell damage caused by oxidative stress. This can reduce the risk of chronic diseases like heart disease and cancer.
4. Blood Sugar Regulation
For those with diabetes, koriandri can be beneficial in managing blood sugar levels. Its ability to improve insulin sensitivity and reduce blood glucose levels is particularly valuable for people looking to maintain or manage their diabetes.
5. Natural Detoxifier
Koriandri is used in natural detox diets due to its ability to promote the removal of toxins, including heavy metals, from the body. This cleansing effect can enhance overall health and energy levels.
6. Promotes Skin Health
Coriander’s antimicrobial properties make it an excellent herb for skin health. It is often used in skincare products to treat acne, reduce inflammation, and improve skin texture. The antioxidants in coriander also help protect the skin from signs of aging.
11. Who Should Use Koriandri?
While koriandri is generally safe for most people, certain individuals may benefit from its use more than others. Here’s a look at who could particularly benefit from adding koriandri to their diet or wellness routine:
1. Individuals with Digestive Issues
If you experience frequent indigestion, bloating, or gas, koriandri could be a useful addition to your diet. Its carminative properties help alleviate digestive discomfort and promote better digestion.
2. People with Diabetes
For those managing diabetes, koriandri may help regulate blood sugar levels, reducing the risk of blood sugar spikes. Including coriander in the diet may support glucose metabolism and insulin sensitivity.
3. Those Seeking to Improve Skin Health
Coriander is often used in skincare routines for its anti-inflammatory and antimicrobial properties. If you struggle with acne or other skin irritations, koriandri may help reduce redness and inflammation.
4. Individuals Looking for Detoxification
Coriander can assist in detoxifying the body by helping eliminate heavy metals and other harmful toxins. If you are following a cleansing regimen or trying to improve liver health, koriandri could play a supportive role.
5. Those with Inflammatory Conditions
People with arthritis, joint pain, or other inflammatory conditions may benefit from coriander’s anti-inflammatory effects. Its compounds can help reduce pain and swelling associated with inflammation.
Conclusion
Koriandri, also known as coriander or cilantro, is a herb that has earned its place in kitchens across the world. Whether used fresh in salads or dried and ground into a spice, its unique aroma and flavor profile make it a valuable ingredient in a wide range of cuisines. With a history that spans thousands of years, from its origins in ancient Egypt to its modern-day use in global cooking, koriandri remains a symbol of culinary heritage and medicinal tradition.
From India to the United States, koriandri is a testament to how plants can transcend cultural boundaries, evolving from ancient remedies to contemporary culinary staples. It’s a herb that not only adds flavor to food but also plays a role in health and wellness, making it much more than just an ingredient.